- バックアップ一覧
- 差分 を表示
- 現在との差分 を表示
- ソース を表示
- 強化学習/Pythonで強化学習する へ行く。
- 1 (2017-10-19 (木) 16:34:09)
- 2 (2017-10-19 (木) 16:42:58)
- 3 (2017-10-23 (月) 10:34:52)
- 4 (2017-10-23 (月) 10:52:07)
- 5 (2018-01-26 (金) 10:44:03)
はじめに †
ここでは、Pythonで強化学習を行います。
例題として、Sutton & Barto の『エージェント・アプローチ人工知能』で用いられている [math]4 \times 3[/math] の迷路を使います。
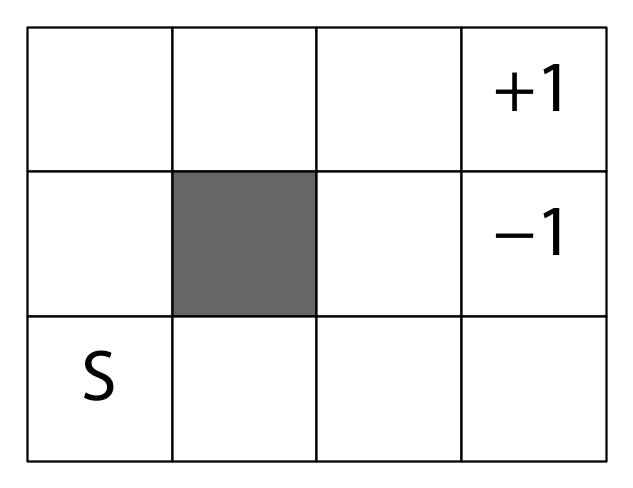
Sのマスが初期状態、+1 と -1 のマスが終端状態です。
行動は東西南北の4種類です。
外側と塗られているマスには壁があり、その方向には進めません。 0.8の確率で選んだ方向に進むことができ、0.1の確率で選んだ方向に対して90度左のマス、0.1の確率でその反対側のマスに進みます。
数値が書かれているマスに到達するとその数値が報酬として得られます。 その他のマスに到達すると報酬 -0.02 が得られます。
強化学習アルゴリズムはQ学習、行動選択は[math]\epsilon[/math]-グリーディーです。
次の環境で確認しました。
- macOS Sierra 10.12.5
- Python 3.5.1
準備 †
NumPyを使いますので、インストールします。
まず、pip3をインストールし、最新版にします。
$ sudo easy_install pip $ sudo pip3 install --upgrade pip
次に、pip3でNumPyをインストールします。
$ sudo pip3 install numpy
クラス構造 †
- 環境を表す Environment
- 迷路を表す Maze
- 強化学習エージェントを表す ReinformentLearningAgent
- Q学習エージェントを表す QLearningAgent
環境 environment.py †
まず初めに、環境を表すクラスがどのような変数とメソッドを持っているかを決めておきます。
変数としては、次のものを持つことにします。
- 状態数 states
- 行動数 actions
メソッドしては、次のものを持つことにします。
- 状態を初期化して返す initState
- 終端状態かどうかを調べる isTerminal
- 報酬を返す getReward
- 行動を実行して次の状態と報酬を返す takeAction
- 状態を文字列で返す strState
- 行動を文字列で返す strAction
- ログを出力する printLog
printLog 以外の実際の実装は、子クラスで行います。
#!/usr/bin/python3 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # # qlagent.py # # Copyright 2017-2018 Tohgoroh Matsui All Rights Reserved. # from rlagent import ReinforcementLearningAgent import numpy as np class QLearningAgent(ReinforcementLearningAgent): """Q学習エージェント。""" def learn(self): """Q学習を用いて学習する。""" env = self.environment # 環境 gamma = self.discount_rate # 割引率 alpha = self.step_size # ステップ・サイズ episodes = 0 # エピソード数 total_steps = 0 # 全ステップ数 self.q = np.zeros([env.states, env.actions]) # Q値をゼロに初期化する while total_steps < self.max_steps: steps = 0 # このエピソードにおけるステップ数 state = env.init_state() # 状態を初期化する while total_steps < self.max_steps and not env.is_terminal(state): # 終端状態になるまで繰り返す: action = self.epsilon_greedy(state) # 行動を選択する reward , state_ = env.take_action(state, action) # 行動を実行し、次の状態と報酬を観測する if self.verbose_level > 1: env.print_log(steps, state, action, reward, state_) # ログを出力する action_ = self.greedy(state_) # 次の状態でQ値が最大の行動を調べる s, a, = env.get_s(state), env.get_a(action) s_, a_ = env.get_s(state_), env.get_a(action_) self.q[s, a] += alpha * (reward + gamma * self.q[s_, a_] - self.q[s, a]) # Q値を更新する state = state_ # 状態を更新する steps += 1 total_steps += 1 if self.evaluation and total_steps % np.power(10, np.floor(np.log10(total_steps))) == 0: eval = self.evaluate() # 評価する print('%d, %f' % (total_steps, eval)) episodes += 1 if self.verbose_level > 0: print(self.q) # Q値を出力 def __init__(self, environment=None, seed=None, discount_rate=0.9, step_size=0.1, epsilon=0.1, max_steps=1000000, evaluation=True, verbose_level=0): super().__init__(environment, seed, discount_rate, step_size, epsilon, max_steps, evaluation, verbose_level)
強化学習エージェント rlagent.py †
強化学習エージェントを表す ReinforcementLearningAgent クラスには、主に行動選択のメソッドを実装します。
学習するためのメソッドは抽象クラスとし、子クラスである QLearningAgent に実装します。
#!/usr/bin/python3 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # # rlagent.py # # Copyright 2017-2018 Tohgoroh Matsui All Rights Reserved. # from abc import ABCMeta, abstractmethod import numpy as np class ReinforcementLearningAgent(metaclass=ABCMeta): """強化学習エージェント。""" @abstractmethod def learn(self): """強化学習を用いて学習する。""" pass def evaluate(self): """学習した行動価値が最も高い行動を選択したときの平均ステップ数を返す。""" env = self.environment # 環境 episodes = 0 # エピソード数 total_steps = 0 # ステップ数 while episodes < 100: # 100エピソード繰り返す: steps = 0 # このエピソードにおけるステップ数 state = env.init_state() # 状態を初期化する state = self.getState(rawState) # 状態を状態番号に while not env.is_terminal(state) and steps < 100: # 状態が終端状態になるか、または、100ステップになるまで繰り返す: action = self.greedy(state) # グリーディーに行動を選択する reward, state_ = env.take_action(state, action) # 行動を実行し、報酬と次の状態を観測する if self.verbose_level > 2: env.printLog(steps, state, action, reward, state_) # ログを出力する state = state_ steps += 1 total_steps += 1 episodes += 1 return total_steps / 100 def uniformly(self): """一様ランダムに行動を選択して返す。""" action = np.random.randint(self.environment.actions) # 0からaction-1までの整数をランダムに生成する return action def greedy(self, state): """グリーディーに行動を選択して返す。""" s = self.environment.get_s(state) # 状態番号 max = self.q[s].max() # 最大のQ値 aIds = np.where(self.q[s] == max)[0] # Q値がmaxである要素のインデックスの配列 r = np.random.randint(len(aIds)) # 0から要素数-1までの整数をランダムに生成する action = aIds[r] # Q値がmaxQである要素のインデックスから行動を選択する return action def epsilon_greedy(self, state): """ε-グリーディー選択を用いて行動を選択して返す。""" r = np.random.rand() # 乱数を生成する action = self.uniformly() if r < self.epsilon else self.greedy(state) # 確率εで一様ランダムに、確率1-εでグリーディーに行動を選択する return action def __init__(self, environment=None, seed=None, discount_rate=0.9, step_size = 0.1, epsilon=0.1, max_steps=1000000, evaluation=True, verbose_level=0): self.environment = environment # 環境 self.seed = seed # 乱数のシード self.discount_rate = discount_rate # 割引率 γ self.step_size = step_size # ステップ・サイズ α self.epsilon = epsilon # ε-グリーディー選択のε self.max_steps = max_steps # 最大ステップ数 self.evaluation = evaluation # 評価 self.verbose_level = verbose_level # ログ出力 self.env = None # 環境 self.q = None # Q値 if self.seed is not None: np.random.seed(seed)
Q学習エージェント qlagent.py †
Q学習エージェントを表す QLearningAgent クラスには、Q学習のアルゴリズムだけを実装します。
Q学習のアルゴリズムは、次のようなものです。
- 行動価値 [math]Q(s, a)[/math] を初期化
- エピソードごとに繰り返し:
- 状態 [math]s[/math] を初期化
- [math]s[/math] が終端状態になるまで繰り返し:
- [math]Q[/math]から導かれる行動選択確率に基づいて [math]s[/math] から行動 [math]a[/math] を選択
- [math]a[/math] を実行し、次の状態 [math]s'[/math] と報酬 [math]r[/math] を観測する
- [math]Q(s, a) \leftarrow Q(s, a) + \alpha \left[ r + \gamma * \max_{a'}Q(s', a') - Q(s, a)\right][/math]
- [math]s \leftarrow s'[/math]
これを、Pythonで実装すると、次のようになります。
#!/usr/bin/python3 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # # environment.py # # Copyright 2017-2018 Tohgoroh Matsui All Rights Reserved. # from abc import ABCMeta, abstractmethod class Environment(metaclass=ABCMeta): """強化学習の環境。""" states = None # 状態数 actions = None # 行動数 @classmethod @abstractmethod def init_state(cls): """初期状態を返す。""" pass @classmethod @abstractmethod def is_terminal(cls): """終端状態ならTrue、そうでないならFalseを返す。""" pass @classmethod @abstractmethod def get_reward(cls, state): """報酬を返す。""" pass @classmethod @abstractmethod def take_action(cls, state, action): """行動を実行して状態を更新し、報酬と次の状態を返す。""" pass @classmethod @abstractmethod def str_state(cls, state): """状態を表す文字列を返す。""" pass @classmethod @abstractmethod def str_action(cls, action): """行動を表す文字列を返す。""" pass @classmethod def print_log(cls, steps, state, action, reward, state_): """ログを出力する。""" print('# %d, %s, %s, %f, %s' % (steps, cls.str_state(state), cls.str_action(action), reward, cls.str_state(state_)))
迷路 maze.py †
#!/usr/bin/python3 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # # maze.py # # Copyright 2017-2018 Tohgoroh Matsui All Rights Reserved. # from environment import Environment import numpy as np class Maze(Environment): """Sutton & Barto 4x3迷路問題。状態は (x座標, y座標) で表される。""" walls = np.array([[0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0]]).T # 壁 terminals = np.array([[ 0, 0, 0, 1], [ 0, 0, 0, 1], [ 0, 0, 0, 0]]).T # 終端状態 # rewards = np.array([[-0.02, -0.02, -0.02, 1.], # [-0.02, 0., -0.02, -1.], # [-0.02, -0.02, -0.02, -0.02]]).T # 報酬 rewards = np.array([[0., 0., 0., 1.], [0., 0., 0., -1.], [0., 0., 0., 0.]]).T # 報酬 width = len(walls) # 迷路の幅 height = len(walls[0]) # 迷路の高さ states = width * height # 状態数 actions = 4 # 行動数 deterministic = True # 状態遷移が決定的 @classmethod def init_state(cls): """初期状態を返す。""" return (0, 2) @classmethod def is_terminal(cls, state): """渡された状態が終端状態ならTrue, そうでないならFalseを返す。""" x, y = state[0], state[1] return True if cls.terminals[x, y] == 1 else False @classmethod def is_wall(cls, state): """渡された状態が壁ならTrue, そうでないならFalseを返す。""" x, y = state[0], state[1] return True if x < 0 or x >= cls.width or y < 0 or y >= cls.height or cls.walls[x, y] == 1 else False @classmethod def get_s(cls, state): """状態を状態番号に変換して返す。""" x, y = state[0], state[1] s = y * cls.width + x return s @classmethod def get_a(cls, action): """行動を行動番号に変換して返す。""" return action @classmethod def get_reward(cls, state): """報酬を返す。""" x, y = state[0], state[1] reward = cls.rewards[x, y] return reward @classmethod def take_action(cls, state, action): """行動を実行して状態を更新し、報酬と次の状態を返す。""" if action == 0: forward = cls.north(state) left = cls.west(state) right = cls.east(state) elif action == 1: forward = cls.east(state) left = cls.north(state) right = cls.south(state) elif action == 2: forward = cls.west(state) left = cls.south(state) right = cls.north(state) else: forward = cls.south(state) left = cls.east(state) right = cls.west(state) if cls.deterministic: state_ = forward else: r = np.random.random() if r < 0.8: state_ = forward elif r < 0.9: state_ = left else: state_ = right reward = cls.get_reward(state_) # 報酬 return reward, state_ @classmethod def str_state(cls, state): """状態を表す文字列を返す。""" x, y = state[0], state[1] return '(%d, %d)' % (x, y) @classmethod def str_action(cls, action): """行動を表す文字列を返す。""" if action == 0: str = 'north' elif action == 1: str = 'east' elif action == 2: str = 'west' else: str = 'south' return str @classmethod def north(cls, state): """北に壁がない場合は北隣の状態を、壁がある場合は現在の状態を返す。""" x, y = state[0], state[1] x_, y_ = x, y - 1 return (x_, y_) if not cls.is_wall((x_, y_)) else state @classmethod def east(cls, state): """東に壁がない場合は東隣の状態を、壁がある場合は現在の状態を返す。""" x, y = state[0], state[1] x_, y_ = x + 1, y return (x_, y_) if not cls.is_wall((x_, y_)) else state @classmethod def west(cls, state): """西に壁がない場合は西隣の状態を、壁がある場合は現在の状態を返す。""" x, y = state[0], state[1] x_, y_ = x - 1, y return (x_, y_) if not cls.is_wall((x_, y_)) else state @classmethod def south(cls, state): """南に壁がない場合は南隣の状態を、壁がある場合は現在の状態を返す。""" x, y = state[0], state[1] x_, y_ = x, y + 1 return (x_, y_) if not cls.is_wall((x_, y_)) else state def __init__(self, deterministic=False): Maze.deterministic = deterministic super().__init__()
実行用ファイル mazeql.py †
#!/usr/bin/python3 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # # mazeql.py # # Copyright 2017-2018 Tohgoroh Matsui All Rights Reserved. # from maze import Maze from qlagent import QLearningAgent import sys if __name__ == '__main__': argvs = sys.argv # コマンドライン引数 seed = None if len(argvs) == 1 else int(argvs[1]) # 乱数のシード maze = Maze(deterministic=True) # 環境 agent = QLearningAgent(environment=maze, seed=seed, verbose_level=1, step_size=0.1, epsilon=0.4) # Q学習エージェント agent.learn() # 学習する
![[PukiWiki] [PukiWiki]](https://xn--p8ja5bwe1i.jp:443/wiki/image/banner.png)